How Solar Power Works?
Main Components of a Solar System
1. Solar Panel
Most modern solar panels are made up of many silicon based photovoltaic cells (PV cells) which generate direct current (DC) electricity from sunlight. The PV cells are linked together within the solar panel and connected to adjacent panels using cables. Note: It is sunlight or irradiance, not heat, which produces electricity in photovoltaic cells. Solar panels, also known as solar modules, are generally connected together in ‘strings’ to create a what is known as a solar array. The amount of solar energy generated depends on several factors including the orientation and tilt angle of the solar panels, efficiency of the solar panel, plus any losses due to shading, dirt and even ambient temperature.
Solar Panels can generate energy during cloudy and overcast weather, but the amount of energy depends on the ‘thickness’ and height of the clouds, which determines how much light can pass through. The amount of light energy is known as solar irradiation and usually averaged over the whole day using the term Peak Sun Hours (PSH). The PSH or average daily sunlight hours depends mainly on the location and time of year.


2. Solar Inverters
Solar panels generate DC electricity which must be converted to alternating current (AC) electricity for use in our homes and businesses. This is primary the role of the solar inverter. In a ‘string’ inverter system, the solar panels are linked together in series, and the DC electricity is brought to the inverter which converts the DC power to AC power. In a micro inverter system, each panel has its own micro-inverter attached to the rear side of the panel. The panel still produces DC, but is converted to AC on the roof and is fed straight to the electrical switchboard.
There are also more advanced string inverter systems which use small power optimisers attached to back of each solar panel. Power optimisers are able to monitor and control each panel individually and ensure every panel is operating at maximum efficiency under all conditions.
3. Solar Batteries / Solar Storage
Batteries used for solar energy storage are available in two main types, lead-acid (AGM & Gel) and lithium-Ion. There are several other types available such as redox flow batteries and sodium-ion but we will focus on the most common two. Most modern energy storage systems use rechargeable lithium-ion batteries and are available in many shapes and sizes which can be configured in several ways
Battery capacity is generally measured is either Amp hours (Ah) for lead-acid, or kilowatt hours (kWh) for lithium-ion. However, not all of the capacity is available for use. Lithium-ion based batteries can typically supply up to 90% of their available capacity per day, while lead-acid batteries generally only supply 30% to 40% of their total capacity per day to increase battery life. Lead-acid batteries can be discharged fully, but this should only be done in emergency backup situations.


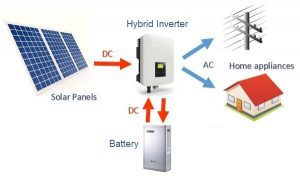
Off-grid solar systems require specialised off-grid inverters and battery systems large enough to store energy for 2 or more days. Hybrid grid-connected systems use lower cost hybrid (battery) inverters, and only require a battery large enough to supply energy for 5 to 10 hours (overnight) depending on the application.
4. Electricity Switchboards
In a common grid-tie solar system, AC electricity from the solar inverter is sent to the switchboard where it is drawn into the various circuits and appliances in your home. This is known as Net metering, where any excess electricity generated by the solar system is sent the electricity grid through an energy meter or stored a battery storage system if you have a hybrid system. Some countries however, use ‘Gross metering’ where all solar energy is exported to the electricity grid.
Hybrid systems can both export excess electricity and store excess energy in a battery. Some Hybrid inverters maybe also be connected to a dedicated backup switchboard which enables some ‘essential circuits’ or critical loads to be powered during a grid outage or blackout.

3 Main Types of Solar Power System
1. On-grid – also known as a grid-tie or grid-feed solar system
2. Off-grid – also known as a stand-alone power system (SAPS)
3. Hybrid – grid-connected solar system with battery storage
On-Grid System
On-grid or grid-tie solar systems are by far the most common and widely used by homes and businesses. These systems do not need batteries and use either solar inverters or micro-inverters and are connected to the public electricity grid. Any excess solar power that you generate is exported to the electricity grid and you usually get paid a feed-in-tariff (FiT) or credits for the energy you export.
Unlike hybrid systems, on-grid solar systems are not able to function or generate electricity during a blackout due to safety reasons. Since blackouts usually occur when the electricity grid is damaged; If the solar inverter was still feeding electricity into a damaged grid it would risk the safety of the people repairing the fault/s in the network. Most hybrid solar systems with battery storage are able to automatically isolate from the grid (known as islanding) and continue to supply some power during a blackout.
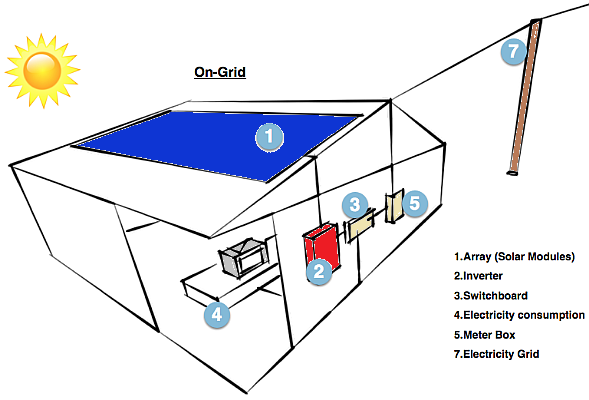
In an on-grid system, this is what happens after electricity reaches the switchboard:
The meter. Excess solar energy runs through the meter, which calculates how much power you are either exporting or importing (purchasing).
Metering systems work differently in many states and countries around the world. In this description I am assuming that the meter is only measuring the electricity being exported to the grid, as is the case in most of Australia. In some states, meters measure all solar electricity produced by your system, and therefore your electricity will run through your meter before reaching the switchboard and not after it. In some areas (currently in California), the meter measures both production and export, and the consumer is charged (or credited) for net electricity used over a month or year period. I will explain more about metering in a later blog.
The electricity grid. Electricity that is sent to the grid from your solar system can then be used by other consumers on the grid (your neighbours). When your solar system is not operating, or you are using more electricity than your system is producing, you will start importing or consuming electricity from the grid.
Off-Grid System
An off-grid system is not connected to the electricity grid and therefore requires battery storage. Off-grid solar systems must be designed appropriately so that they will generate enough power throughout the year and have enough battery capacity to meet the home’s requirements, even in the depths of winter when there is generally much less sunlight.
The high cost of batteries and off-grid inverters means off-grid systems are much more expensive than on-grid systems and so are usually only needed in more remote areas that are far from the electricity grid. However battery costs are reducing rapidly, so there is now a growing market for off-grid solar battery systems even in cities and towns.
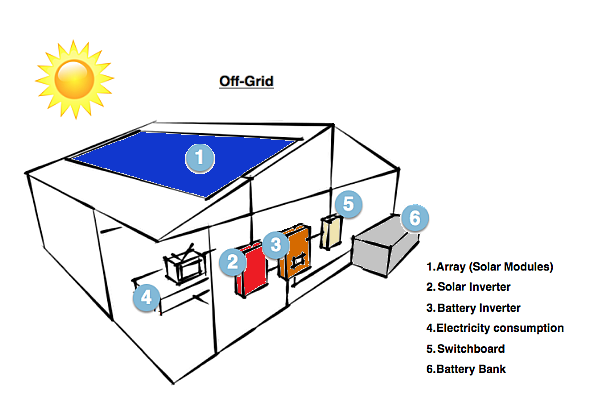
The battery bank. In an off-grid system there is no public electricity grid. Once solar power is used by the appliances in your property, any excess power will be sent to your battery bank. Once the battery is full it will stop receiving power from the solar system. When your solar system is not working (night time or cloudy days), your appliances will draw power from the batteries.
Backup Generator. For times of the year when the batteries are low on charge and the weather is very cloudy you will generally need a backup power source, such as a backup generator or gen-set. The size of the gen-set (measured in kVA) should to be adequate to supply your house and charge the batteries at the same time.
Hybrid System
Modern hybrid systems combine solar and battery storage in one and are now available in many different forms and configurations. Due to the decreasing cost of battery storage, systems that are already connected to the electricity grid can start taking advantage of battery storage as well. This means being able to store solar energy that is generated during the day and using it at night. When the stored energy is depleted, the grid is there as a back up, allowing consumers to have the best of both worlds. Hybrid systems are also able to charge the batteries using cheap off-peak electricity (usually after midnight to 6am).
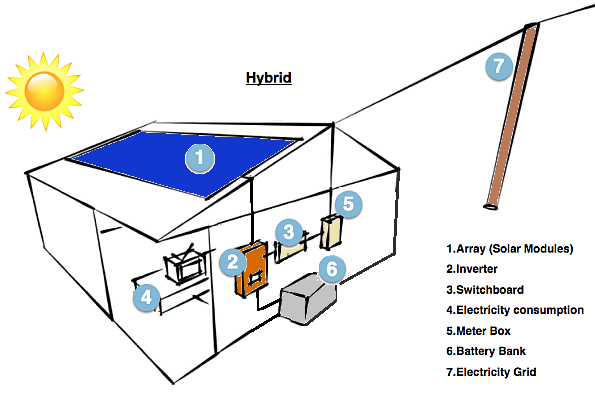
The battery bank. In a hybrid system once the solar power is used by the appliances in your property, any excess power will be sent to the battery bank. Once the battery bank is fully charged, it will stop receiving power from the solar system. The energy from the battery can then be discharged and used to power your home, usually during the peak evening period when the cost of electricity is typically at it’s highest.
The meter and electricity grid. Depending on how your hybrid system is set up and whether your utility allows it, once your batteries are fully charged excess solar power not required by your appliances can be exported to the grid via your meter. When your solar system is not in use, and if you have drained the usable power in your batteries your appliances will then start drawing power from the grid.